Why risk management is important
Advantages and disadvantages of risk management in trading
How to use risk management in trading
Risk management, also known as money management, refers to a number of trading techniques employed to lessen risk exposure. Being affected by various factors, currency rates may be quite volatile at times; thus, protecting your account against adverse price fluctuations is an essential part of a trading strategy.
Risk management is like having a safety plan to preserve capital in case the trade does not play out. Traders use various strategies and technical analysis tools to protect their money and any profits they might make. Since currency prices can change unexpectedly, having a good risk management plan helps them avoid losing much money. The core concept of money management is to avoid risking more than 1–2% of personal funds on any single trade. This principle may significantly reduce risk exposure: provided that only 1% of the initial deposit is at risk, even after several losing trades, you are likely to retain the majority of the account balance. Let's elaborate on this further with an example. Suppose you have a trading strategy that is 90% successful. In a sample of 100 trades, if one is risking 10% per trade, there is a possibility one might have a run of 5 losses. This would translate to a 50% loss of capital. Therefore, it is necessary to have a solid risk management strategy in Forex. Trading Forex without risk management is simply gambling. Risk Reward Ratio denotes the potential profit in comparison to the amount you may lose for any given trade. For example, when you risk 100 USD in a position to potentially gain 300 USD, the risk-to-reward ratio is 1:3. A ratio of 1:2 is considered the minimum one should aim for, as only a third of positions would need to be profitable to remain break-even.What is risk management?
Risk Reward Ratio (RRR)
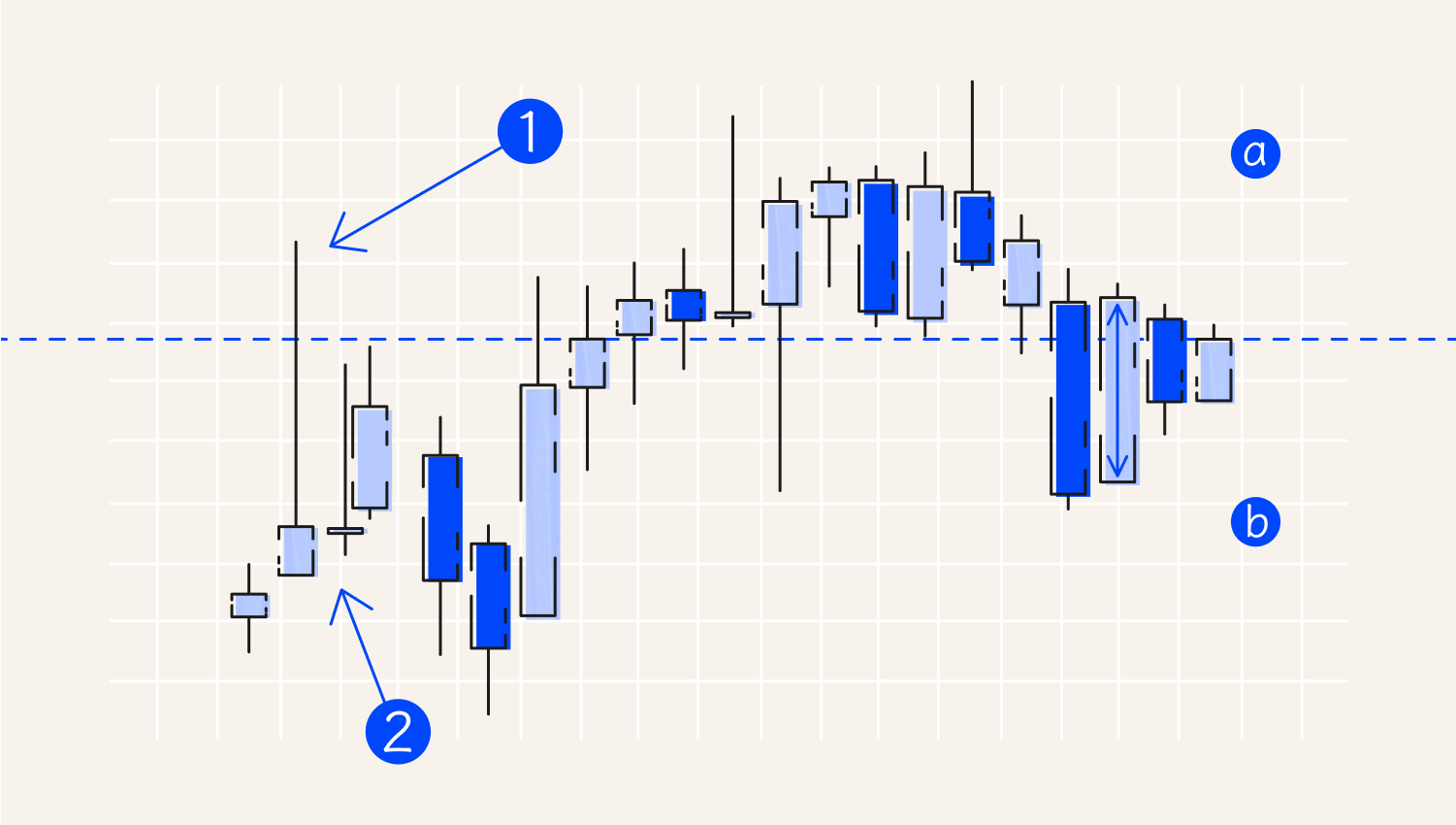
As shown above, the take-profit level marked 2 should be twice as high as the stop-loss level marked 1. Stop-loss and take-profit orders close the position when the price reaches the predefined level a trader sets. This way, stop-loss and take-profit levels can define potential profit and loss.
Here is why risk management is the core element of trading:Why risk management is important
Reason
Explanation
Keeping your capital safe
Good risk management prevents large losses that can wipe out an account. Protecting capital is key to staying in the game and building long-term profits.
Staying calm
Clear risk limits reduce stress and help maintain focus. Without them, losses can trigger emotional decisions that often lead to even bigger setbacks.
Steady returns
Instead of wild swings, risk control supports more consistent gains. It helps not just avoid losses but also protect profits already made.
Smart risk-taking
Limiting risk per trade encourages more thoughtful choices. It shifts focus from gambling to selecting trades that align with a solid strategy.
Handling uncertainty
Markets are unpredictable. Good risk management prepares for surprises, spreads exposure, and reduces the impact of sudden events.
Learning and growing
Mistakes are part of the process. Controlled risk allows for learning without devastating losses, making it easier to improve over time.
Sticking to your plan
Risk limits support disciplined trading by keeping emotions in check and preventing impulsive decisions during volatile moments.
Surviving tough times
Every trader faces losses. Risk management helps weather nasty streaks and stay ready for future opportunities.
Building confidence
Consistently managing risk builds trust in the process. Confidence grows when losses stay manageable and results improve over time.
Long-term success
Lasting success comes from steady growth, not quick wins. Managing risk keeps losses small and allows profits to accumulate.
Here are the steps to take to manage risks while trading. To calculate position size, traders usually consider: Position sizing is calculated using the following formula:Risk management process
Here are the positive aspects of using risk management in your trades: Risk management limits how much can be lost on any single trade, helping preserve your account over time. With clear limits in place, it's easier to stay calm and avoid impulsive decisions during market volatility. Surviving losses without wiping out your account allows you to keep trading, learning, and compounding profits. A solid risk plan keeps your strategy grounded in logic, not emotion or guesswork. Here are the challenges of RM in trading: Being overly cautious can sometimes mean exiting trades too early or missing out on bigger gains, especially with tight stop-losses. For beginners, understanding and applying risk management tools can be complex. It takes time, study, and practice to do it well. Effective risk management often means monitoring trades, adjusting strategies, and staying updated with market changes. Having a risk plan doesn't eliminate all risks. Markets are unpredictable, and losses can still happen even with strong risk controls in place. Some risk management tools, like hedging or trade insurance, come with fees that can reduce overall profit margins.Advantages and disadvantages of risk management in trading
Here are the key strategies you can apply in Forex trading to protect your money and succeed long-term. Use a stop loss. The stop loss is a predetermined price at which the trade closes to limit further losses. For example, if you buy a currency at a specific price and set a stop loss at a lower price, it helps limit your losses. If you buy EURUSD at 1.19500 and set your stop-loss order at 1.1930, you're risking 20 pips (a tiny measure of price change). Position sizing means calculating the lot size one should take. Forex traders consider these factors to calculate position size. The example below shows how to calculate position size. Below, we calculate the position size (Lot Size) EURUSD example: EURGBP example: Hedging is like having a backup plan to protect your trades. If there's a risk the price might drop, you can hedge in two main ways: holding opposite positions or using options. Holding opposite positions means buying and selling the same currency pair at the same time. If one position loses value, the other can help offset those losses. Using options works like insurance for your trade. For example, if you expect a currency's price to rise but worry it might fall due to upcoming news, you can buy an option that gives you the right to sell it at a set price later. This protects you if the price drops. Leverage lets you control a lot more money than you actually have. It's like borrowing money to make more significant trades. While it can increase your profits, it can also increase your losses. So, it's important to use leverage carefully. Think of it like driving a fast car. It's exciting, but you need to be responsible to avoid accidents.How to use risk management in trading
Stop-loss orders
Position sizing
Hedging
Leverage
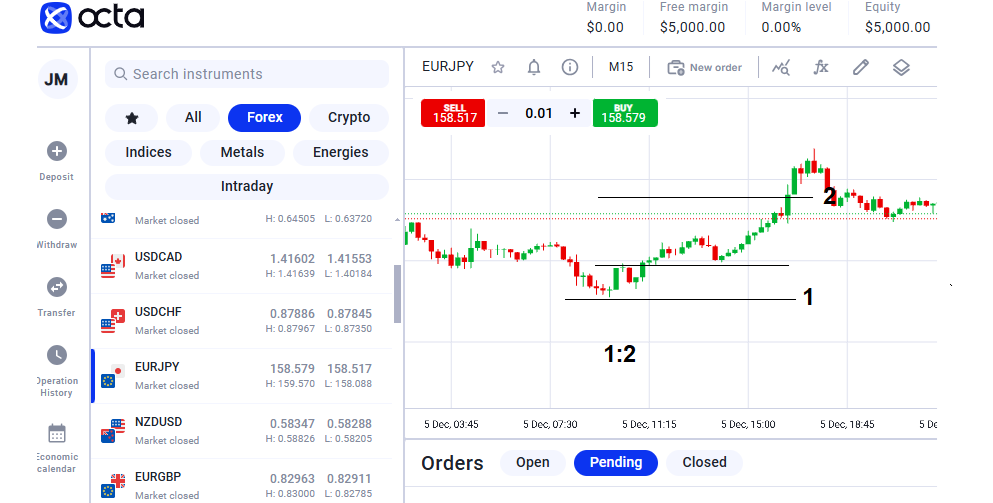
Let's say you open 1 lot EURUSD Buy order at 1.12097. To achieve a risk-to-reward ratio of 1:2, you can set the stop-loss level at 1.12077 (2 pips) and take the profit level at 1.12137 (4 pips). Thus, you will only be risking 20 USD to gain 40 USD. Depending on your initial deposit, you can set SL/TP levels even further as long as your risk is below 1–2% of your personal funds.Examples
1. Potential loss 20 USD
2. Potential profit 40 USD
a. risk
b. reward
It is important to note that the price of each pip depends on the trading tool and the volume of your position. You can find the pip price per 1 lot on the Spreads and Conditions page or simply calculate it using a trading calculator.
A trailing stop can be used to adjust the stop-loss level automatically whenever the price moves in a favourable direction. This reduces the risks and may eventually lock in the profit already gained.
Keep in mind, however, that neither stopping loss nor taking profit is guaranteed: when the market is volatile or during a price gap, your order may be executed at a price different than expected.
You can learn more about events and indicators that affect market volatility in this article.
Final thoughts





